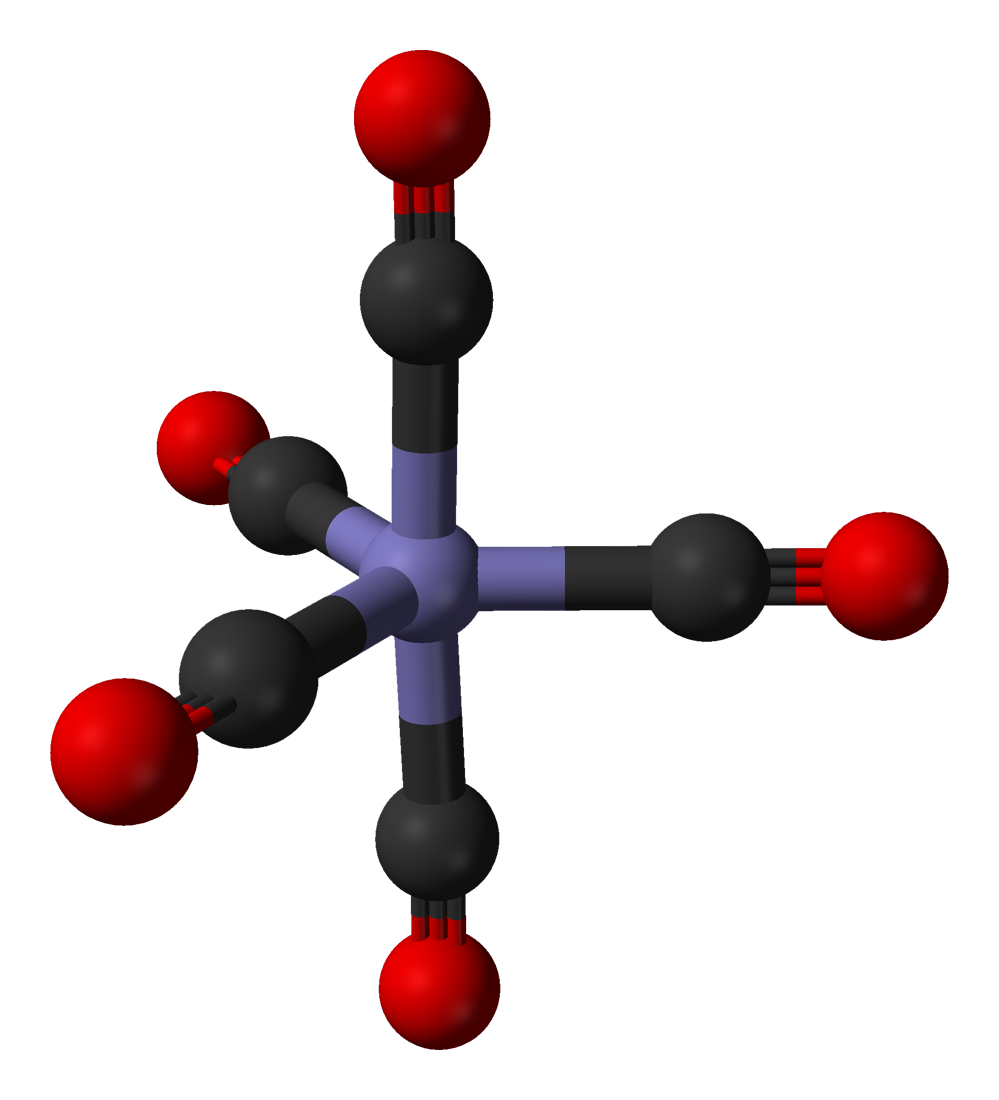
Fe(CO)5
Iron Pentacarbonyl is an intermediate that has found utility in a variety of applications. IPC it has been used as a fuel antiknock agent, a photochemical additive, and an intermediate for many iron products.
The most important applications are:
- Catalyst: A wide variety of reactions are catalyzed for coal liquefaction, Fischer-Tropsch hydroformylation, olefin isomerization and water gas shift reactions.
- Precursor: A starting material for chemically pure iron, iron oxides, iron catalysts and thin iron films.
- Reagent: Reacts with air, alkali, amines, carbon tetrachloride, halogens, hydrogen, mercaptans, mercury salts and other salts.
- Desulfurization: of sulfur from coal and petroleum products.
- Waste Remediation: Halogen solvent waste remediation.
Physical Properties
Boiling point: 103 °C
Melting point: -20 °C
Specific gravity: 1.453
Chemistry
Iron Pentacarbonyl is a specialty chemical that is produced as an intermediate during the manufacture of carbonyl iron powders. It is produced from a high-pressure reaction between high-grade iron and carbon monoxide. This organometallic compound exists as a liquid at room temperature. It may ignite spontaneously in air and is decomposed by heat to metallic iron and carbon monoxide. In air it decomposes to iron oxides and in sunlight to iron nonacarbonyl. While Fe(CO)5 is highly reactive, it is stable in dark storage under nitrogen. It is soluble in common organic solvents such as acetone or toluene and insoluble in water or liquid ammonia. It is unreactive with most acids.
Physical Properties
Boiling point: 103 °C
Melting point: -20 °C
Specific gravity: 1.453

Chemistry
Iron pentacarbonyl is a specialty chemical that is produced as an intermediate during the manufacture of carbonyl iron powders. It is produced from a high-pressure reaction between high-grade iron and carbon monoxide. This organometallic compound exists as a liquid at room temperature. It may ignite spontaneously in air and is decomposed by heat to metallic iron and carbon monoxide. In air it decomposes to iron oxides and in sunlight to iron nonacarbonyl. While Fe(CO)5 is highly reactive, it is stable in dark storage under nitrogen. It is soluble in common organic solvents such as acetone or toluene and insoluble in water or liquid ammonia. It is unreactive with most acids.

